OttoKit WordPress Plugin Vulnerability, CVE-2025-27007
May 20, 2025
By Bruce Skillern
CVE-2025-27007 is a critical unauthenticated privilege escalation vulnerability affecting the OttoKit WordPress plugin (formerly SureTriggers), which is used by over 100,000 websites for workflow automation and third-party integration. The vulnerability exists in the plugin’s create_wp_connection() function, which fails to properly verify user authentication when application passwords are not configured. This allows unauthenticated remote attackers to create administrator accounts on vulnerable websites (Patchstack, 2025a; The Hacker News, 2025).
The vulnerability, initially disclosed on April 11, 2025, was patched on April 21, 2025, with version 1.0.83 of the plugin. Exploitation was observed just 91 minutes after public disclosure, highlighting the rapid response time of malicious actors (Patchstack, 2025a).
Vulnerability Type (CWE)
- CWE-266: Incorrect Privilege Assignment. This refers to scenarios in which a software product assigns higher-than-appropriate privileges to a user or process, as seen in OttoKit’s failure to verify credentials via
wp_authenticate_application_password()(NVD, 2025).
CVSS Score
Base Score : 9.8 (Critical)
Attack Vector: Network
Attack Complexity: Low
Privileges Required: None
User Interaction: None
Scope: Unchanged
Impact on CIA:
- Confidentiality: High
- Integrity: High
- Availability: High
Impacted Versions
- All versions of OttoKit (formerly SureTriggers) up to and including 1.0.82 are affected (Patchstack, 2025a).
Mitigation Steps
- Update Plugin: Upgrade to OttoKit version 1.0.83 or later, which addresses the vulnerability by adding access key validation and fixing logic flaws in the REST API authentication (Patchstack, 2025b)
- Audit User Accounts: Review all administrator-level accounts for suspicious usernames like otto-connect, wp-bot-user, or admin_support (Infoziant, 2025).
- Monitor Logs: Check for POST requests to
/wp-json/sure-triggers/v1/connection/create-wp-connectionand/automation/action, particularly with suspicious payloads (Patchstack, 2025a). - Restrict Access: If possible, restrict access to these REST API endpoints from untrusted IP addresses.
Exploit Process
- Initial Exploit: Attackers send a POST request to
/wp-json/sure-triggers/v1/connection/create-wp-connection, passing guessed or arbitrary usernames, passwords, and fake access keys. The request bypasses authentication if no application password has ever been configured (The Hacker News, 2025). - Privilege Escalation: A follow-up POST request to
/wp-json/sure triggers/v1/automation/actionincludes the payload: "type_event": "create_user_if_not_exists", silently creating a new administrator account on the targeted site (GitHub, 2025).
Timeline
- April 11, 2025: Vulnerability reported to Patchstack by researcher Denver Jackson.
- April 12, 2025: Vendor notified and began developing a patch.
- April 21, 2025: Patch released in OttoKit version 1.0.83.
- April 24, 2025: Forced updates deployed to most plugin users.
- May 2, 2025: Public disclosure of the vulnerability.
- May 2, 2025: Exploitation observed approximately 91 minutes after disclosure (Patchstack, 2025a).
TTPs & IOCs
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures
- Privilege Escalation: The vulnerability stems from improper validation in
create_wp_connection()and misuse of thewp_authenticate_application_password()function (Patchstack, 2025b). - Authentication Bypass: Exploits are successful only if application passwords have never been configured and if OttoKit has never been connected with an application password(The Hacker News, 2025).
- Post-Exploitation Persistence: Admin accounts are created silently and can be used to install malware, exfiltrate data, or maintain long-term access (Infoziant, 2025).
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs):
- Suspicious REST API Calls:
/wp-json/sure-triggers/v1/connection/create-wp-connection/wp-json/sure-triggers/v1/automation/action(Patchstack, 2025b)
- Malicious Payloads:
- Requests containing "type_event": "create_user_if_not_exists” (GitHub, 2025)
- Requests containing "type_event": "create_user_if_not_exists” (GitHub, 2025)
- Unauthorized Administrator Accounts:
- Usernames such as otto-connect, wp-bot-user, admin_support (Infoziant, 2025)
- Usernames such as otto-connect, wp-bot-user, admin_support (Infoziant, 2025)
- Known Malicious IP Addresses:
- 2a0b:4141[:]820:1f4::2
- 41.216.188[.]205
- 144.91.119[.]115
- 194.87.29[.]57
- 196.251.69[.]118
- 107.189.29[.]12
- 205.185.123[.]102
- 198.98.51[.]24
- 198.98.52[.]226
- 199.195.248[.]147 (The Hacker News, 2025)
Centripetal’s Perspective
Centripetal’s threat intelligence telemetry confirms early and comprehensive detection of OttoKit CVE-2025-27007 exploit activity, achieving 100% coverage of all known malicious IP addresses linked to the campaign. Nine unique IPs identified as indicators of compromise (IOCs) were observed in our Active Intelligence data, with first-seen dates spanning April 1 to May 6, 2025. Notably, eight of the nine IOCs were associated with reconnaissance activity, consistent with pre-exploitation scanning behavior used to identify unpatched WordPress instances running misconfigured OttoKit plugins. This reconnaissance heavy tactic supports a mass exploitation strategy driven by automation. Centripetal’s telemetry observed activity from six of the nine identified IP-based indicators of compromise (IOCs), with particularly aggressive behavior from IP address 41.216.188[.]205. This address accounted for over 87% of the top-triggering events across our customer base and was linked to repeated reconnaissance and scanning activity against WordPress sites. Public abuse databases confirm that this IP has been reported over 100 times by dozens of independent sources for web application attacks and brute-force behavior, with incidents logged as recently as May 19, 2025. Its consistent targeting of /wp-content/uploads/ and repeated 404 error generation aligns with adversarial probing techniques designed to locate unpatched OttoKit plugin deployments.
Centripetal’s telemetry observed activity from six of the nine identified IP-based indicators of compromise (IOCs), with particularly aggressive behavior from IP address 41.216.188[.]205. This address accounted for over 87% of the top-triggering events across our customer base and was linked to repeated reconnaissance and scanning activity against WordPress sites. Public abuse databases confirm that this IP has been reported over 100 times by dozens of independent sources for web application attacks and brute-force behavior, with incidents logged as recently as May 19, 2025. Its consistent targeting of /wp-content/uploads/ and repeated 404 error generation aligns with adversarial probing techniques designed to locate unpatched OttoKit plugin deployments.
The observed IOCs primarily reflect mass-scanning infrastructure likely tied to automated exploitation campaigns. Most exhibited early-stage reconnaissance behavior, such as admin panel enumeration and account creation attempts. This reinforces the adversary’s objective of broad targeting over tailored attacks, increasing the operational value of early IOC detection and containment.
 From a sector perspective, the education industry comprised 96.9% of affected telemetry, underscoring adversaries’ focus on academic institutions, which often operate complex WordPress infrastructures.
From a sector perspective, the education industry comprised 96.9% of affected telemetry, underscoring adversaries’ focus on academic institutions, which often operate complex WordPress infrastructures.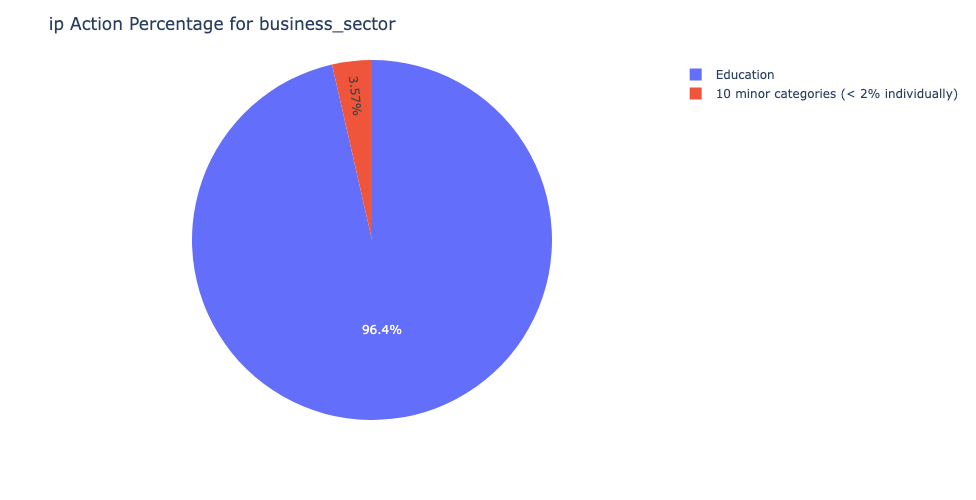
Centripetal customers using Active Threat Defense were proactively protected, with policy enforcement and behavioral detection mechanisms neutralizing threats well before public disclosure on May 2, 2025.
The exploitation of CVE-2025-27007 reinforces the persistent threat posed by unauthenticated API vulnerabilities in widely used plugins like OttoKit. With a CVSS score of 9.8 and no requirement for user interaction or prior access, this vulnerability exemplifies how minor configuration oversights can lead to full site compromise. The speed of exploitation, less than two hours post-disclosure, highlights the operational readiness of threat actors to weaponize public vulnerabilities at scale.
Organizations relying on WordPress, particularly within the education sector, must remain alert. Immediate remediation through plugin updates, log auditing, and strict REST API controls are critical steps to reducing exposure. This incident also underscores the importance of layered defenses. Centripetal’s Active Threat Defense demonstrated how proactive, intelligence-driven security measures can detect, classify, and contain malicious activity before exploitation gains traction. As threat actors continue to automate their attack chains, defenders must match their speed and precision with equally agile and adaptive protections.
If you are a current user of WordPress and use OttoKit plugin, please contact support@centripetal.ai.
Centripetal is also pleased to offer Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Assessment services to help organizations identify vulnerabilities and reduce risk. If interested, please contact our Professional Services team at profservs@centripetal.ai or reach out to your Centripetal Account Representative.
Resources
- https://github.com/absholi7ly/CVE-2025-27007-OttoKit-exploit
- https://thehackernews.com/2025/05/ottokit-wordpress-plugin-with-100k.html
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-27007
- https://patchstack.com/database/wordpress/plugin/suretriggers/vulnerability/wordpress-suretriggers-1-0-82-privilege-escalation-vulnerability?_s_id=cve
- https://patchstack.com/articles/additional-critical-ottokit-formerly-suretriggers-vulnerability-patched
- https://medium.com/@infoziant/ottokit-wordpress-plugin-vulnerability-cve-2025-27007-attackers-adding-admin-accounts-on-3356cd38c08f
Know what’s coming. Stop what’s next.
Sign up for our free threat alert bulletin service here.
The Cybercrime Barrier Your Organization Deserves
Sign up for a custom demonstration from our security team of how we bring together the best minds and most complete collection of threat intelligence to provide you with a shocking level of relief.