By Nithin Ravi
CVE-2025-5777, nicknamed CitrixBleed 2, is a critical vulnerability observed since early June in Citrix Netscaler ADC and Gateway instances. Citrix has fixed this vulnerability in their latest update and it is recommended to immediately upgrade NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway appliances to the recommended patched versions.
With a 9.3 score on CVSS v4.0, CVE-2025-5777 is an insufficient input validation vulnerability that leads to a memory overread issue. This critical flaw allows an unauthenticated attacker to remotely read sensitive memory contents from vulnerable NetScaler appliances.
The original “CitrixBleed” vulnerability (CVE-2023-4966), was exploited by various ransomware groups and nation-state actors which led to significant data breaches across different industrial sectors. Considering this previous impact, it is strongly recommended to implement the mitigation steps for CitrixBleed 2 before any attacker takes advantage of the vulnerability.
Vulnerability Type (CWE)
CWE-125: CVE-2025-5777 is a vulnerability where the program doesn’t check the size of the input data correctly. This leads to a memory overread, meaning it tries to read data from out-of-bounds memory locations it shouldn’t access.
The vulnerability is specifically triggered when the NetScaler appliance is configured as a Gateway (serving as a VPN virtual server, ICA Proxy, CVPN, or RDP Proxy) or an AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Auditing) virtual server.
CVSS Score
Base Score: 9.3 (Critical)
Attack Vector: Network (AV:N)
Attack Complexity: Low (AC:L)
Privileges Required: None (PR:N)
User Interaction: None (UI:N)
Scope: Unchanged (S:U)
Impact on CIA: High
- Confidentiality: High (SC:H)
- Integrity: High (SI:H)
- Availability: High (SA:H)
Impacted Versions
The CVE-2025-5777 vulnerability specifically affects Citrix NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway appliances. It is crucial for organizations to identify if their deployments fall within the vulnerable product lines and specific build versions.
Citrix notified people of the affected and patched versions:
| Impacted Versions | Patched Versions |
|---|---|
| NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway | NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway |
| 14.1 prior 14.1-43.56 | 14.1-43.56 and later releases |
| NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway | NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway |
| 13.1 prior 13.1-58.32 | 13.1-58.32 and later releases of 13.1 |
| NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS and NDcPP | NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS and NDcPP |
| prior 13.1-37.235-FIPS | 13.1-37.235 and later releases of 13.1-FIPS and 13.1-NDcPP |
| NetScaler ADC 12.1-FIPS | NetScaler ADC 12.1-FIPS |
| prior 12.1-55.328-FIPS | 12.1-55.328 and later releases of 12.1-FIPS |
Mitigation Steps
Addressing this critical vulnerability requires immediate action. The first step is to upgrade all the affected NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances to the latest/recommended patched versions. For appliances configured as Gateway or AAA virtual servers, there are no other available mitigations besides applying these patches.
Citrix also recommends to terminate all active ICA and PCoIP sessions after all NetScaler appliances in the HA pair or cluster have been upgraded to the fixed builds. These can be achieved by running the below mentioned commands:
kill icaconnection -all
kill pcoipConnection -all
kill rdp connection -all
kill ssh connection -all
kill aaa session -all
kill telnetConnection -all
kill connConnection -all
Post upgrading and terminating sessions, organizations can also implement the following security measures:
- Restriction of network access to the NetScaler Management Interface to reduce its exposure.
- Implementation of additional network segmentation to isolate critical systems thereby limit the potential of attackers to perform lateral movement.
- Deployment or update WAF to filter for malicious traffic and block known exploitation patterns associated with the CVE.
- Continuous monitoring for any suspicious network activities, unauthorized access attempts targeting NetScaler devices.
Exploit Process
The CitrixBleed 2 vulnerability leverages a memory management flaw to achieve pre-authentication memory disclosure, which can lead to authentication bypass and session hijacking.
An unauthenticated attacker would use the following steps to exploit this vulnerability:
- Send an HTTP POST request to the
/p/u/doAuthentication.doendpoint and omit the value for theloginparameter. Typically a normal user would uselogin=usernameas the query parameter, but the attacker would omit the username value and just use the login as a parameter by itself. This triggers a error in the backend, causing a memory variable to remain uninitialized. - Monitor the server’s response which is typically an XML-formatted data and lookout for the value inside
<InitialValue>XML element which leaks memory content
Each request is observed to leak roughly around 127 bytes of memory from the stack which includes sensitive data such as session cookies, auth tokens and much more.
Timeline
- June 17, 2025: The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) publishes initial details for CVE-2025-5777, describing it as an insufficient input validation vulnerability leading to memory overread.
- June 24, 2025: The CVE begins to trend in security discussions within the cybersecurity community.
- June 26, 2025: Citrix, in an official blog post, states that as of this date, there is “no evidence to suggest exploitation of CVE-2025-5777.
- July 10, 2025: The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) adds CVE-2025-5777 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, officially confirming its active exploitation in the wild.
TTPs & IOCs
The Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) employed by attackers exploiting CVE-2025-5777 is as follows:
- Initial Access via Malformed Requests The exploit is initiated by crafting a malicious HTTP request to NetScaler Gateway or AAA Virtual servers which contain a malformed login parameter.
- Memory Leakage and Token Theft The vulnerability allows attackers to repeatedly leak small chunks of memory (approximately 127 bytes per request)
- Session Hijacking and MFA Bypass Using the stolen session tokens, attackers can hijack existing authenticated sessions. With an active session token, attackers can also bypass MFA checks and gain access to internal networks.
- Post-Exploitation After establishing initial access, attackers have been seen performing extensive Active Directory reconnaissance which includes utilizing tools such as ADExplorer64.exe, using LDAP queries and more.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs):
45.135.232[.]205
38.54.59[.]96
78.128.113[.]30
89.7.196[.]73
124.77.248[.]219
45.93.30[.]243
45.93.30[.]98
39.187.211[.]197
45.134.26[.]35
196.251.118[.]160
45.93.30[.]40
154.38.121[.]214
121.237.80[.]248
91.219.238[.]78
38.244.138[.]83
Centripetal’s Perspective
At Centripetal, staying ahead of emerging cyber threats is our commitment to your security. We constantly monitor the threat intelligence and our recent observations around the CitrixBleed 2 vulnerability highlight the importance of proactive threat intelligence in keeping everyone safe.
Centripetal’s threat intelligence telemetry confirms early and comprehensive detection of the CitrixBleed 2 CVE-2025-5777 vulnerability, achieving 100% coverage of all known malicious IP addresses linked to the campaign.
Shortly after CISA added CVE-2025-5777 to the Known Exploited Vulnerability (KEV) catalog, we saw a huge surge in the exploitation attempts. GreyNoise’s statistics show a huge spike in the activity on the 8th of July, reaching it’s highest peak on July 11.
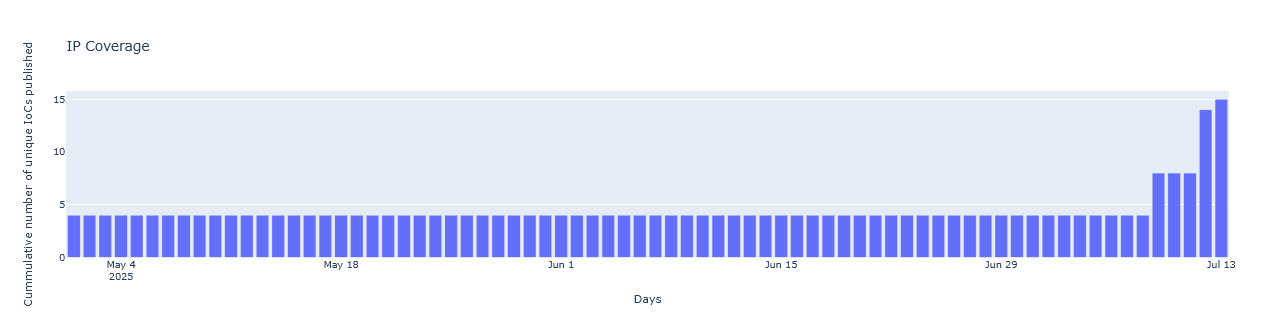
However, long before the vulnerability was widely recognized, our active threat intelligence data began flagging suspicious activity. As early as the 4th of May, we observed Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) related to the CitrixBleed 2 vulnerability. Despite multiple IOCs being observed in our intelligence data, 15 of them particularly have been found to perform malicious activities and not merely crawling or scanning.
Our ability to provide such robust protection is powered by a diverse array of threat intelligence sources. We collaborate with leading threat intelligence providers such as GreyNoise, Recorded Future, and many others
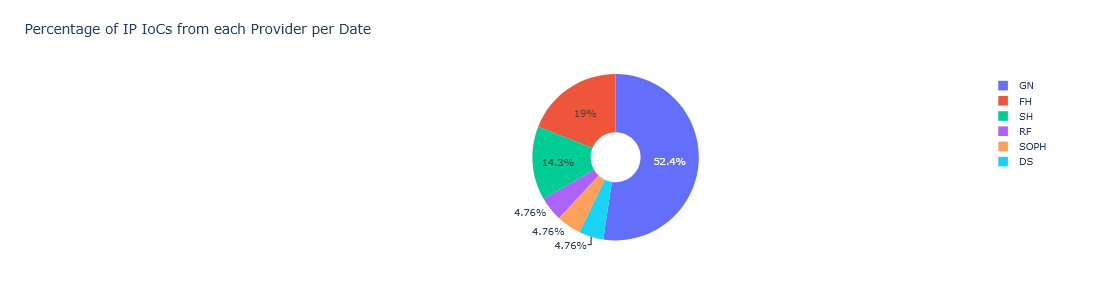
With a high score of 9.3 on the CVSS scale and having a no-user interaction exploit process with low-complexity attack chain, this vulnerability has become an extremely attractive target for bad actors, including sophisticated ransomware groups. This memory leak vulnerability has the potential to leak sensitive information such as tokens, credentials and much more.
At the time of writing, this vulnerability is actively exploited much like the original CitrixBleed which surfaced on 2023. Threat actors exploiting this vulnerability have largely been targeting the financial sector but also go after the vulnerable versions of NetScaler appliances across multiple industries including federal agencies.
Centripetal urges its customers to patch the vulnerable instances and recommends terminating various sessions such as the ICA, PCoIP, RDP, SSH and others as listed in the Mitigation Steps section. Centripetal also provides 100% coverage to all the known indicators of compromise associated with this vulnerability.
If you are a current client of Citrix NetScalar please contact support@centripetal.ai.
Centripetal is also pleased to offer Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Assessment services to help organizations identify vulnerabilities and reduce risk. If interested, please contact our Professional Services team at profservs@centripetal.ai or reach out to your Centripetal Account Representative.
Public Resources
- https://support.citrix.com/support-home/kbsearch/article?articleNumber=CTX693420
- https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/alerts/2025/07/10/cisa-adds-one-known-exploited-vulnerability-catalog
- https://labs.watchtowr.com/how-much-more-must-we-bleed-citrix-netscaler-memory-disclosure-citrixbleed-2-cve-2025-5777/
- https://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2025-5777/
- https://thehackernews.com/2025/07/cisa-adds-citrix-netscaler-cve-2025.html
- https://www.imperva.com/blog/cve-2025-5777-exposes-citrix-netscaler-to-dangerous-memory-leak-attacks/
- https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/citrixbleed-2-vulnerability/
- https://horizon3.ai/attack-research/attack-blogs/cve-2025-5777-citrixbleed-2-write-up-maybe/
- https://arcticwolf.com/resources/blog-uk/follow-up-updates-on-actively-exploited-information-disclosure-vulnerability-citrix-bleed-2-in-citrix-netscaler-adc-and-gateway/